Cosmetic surgery encompasses a wide range of procedures aimed at enhancing physical appearance, improving symmetry, and addressing the effects of aging. Below is an overview of the most common cosmetic surgeries, detailing the procedures and explaining why individuals might choose to undergo them.
1. Facelift (Rhytidectomy)
Procedure Overview:
A facelift aims to reduce the signs of aging by tightening facial tissues, removing excess skin, and smoothing deep folds. The surgery rejuvenates the lower two-thirds of the face and the neck.
Steps:
- Anesthesia: Performed under general anesthesia or local anesthesia with sedation.
- Incisions: Typically made around the hairline and ears, sometimes extending to the lower scalp.
- Tissue Tightening: The underlying muscles and tissues are lifted and secured in a more youthful position.
- Skin Redraping: Excess skin is trimmed away, and the remaining skin is re-draped for a smoother appearance.
- Closure: Incisions are closed with sutures, and the scars are typically hidden within the hairline and natural contours.
Why Patients Choose It:
- To address sagging skin, deep wrinkles, and jowls.
- To restore a more youthful and refreshed appearance.
- To boost confidence and feel younger.
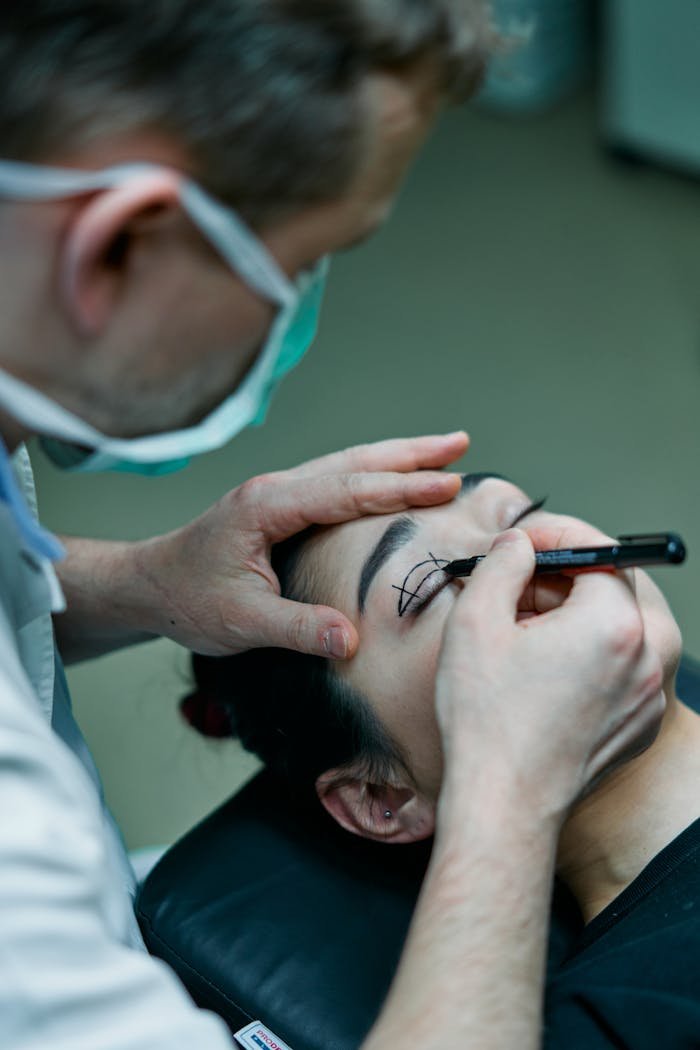
2. Blepharoplasty (Eyelid Surgery)
Procedure Overview:
Blepharoplasty is a surgery designed to correct drooping eyelids and remove puffiness by removing excess skin, fat, and muscle from the upper and/or lower eyelids.
Steps:
- Anesthesia: Usually performed under local anesthesia with sedation, sometimes general anesthesia.
- Incisions: For the upper eyelids, incisions are made in the natural crease; for the lower eyelids, they are made just below the lash line or inside the eyelid.
- Tissue Removal: Excess skin and fat are removed or repositioned, and muscles may be tightened.
- Closure: Incisions are closed with fine sutures, which are typically removed within a week.
Why Patients Choose It:
- To eliminate droopy upper eyelids that may impair vision.
- To remove bags under the eyes, creating a more alert and youthful look.
- To enhance overall facial aesthetics.
3. Rhinoplasty (Nose Reshaping Surgery)
Procedure Overview:
Rhinoplasty reshapes the nose to improve its appearance or function. It can address issues such as the size, shape, or proportion of the nose.
Steps:
- Anesthesia: General or local anesthesia with sedation.
- Incisions: Incisions are usually made inside the nostrils (closed rhinoplasty) or across the columella, the tissue between the nostrils (open rhinoplasty).
- Reshaping: The surgeon reshapes the bone and cartilage to achieve the desired shape.
- Closure: Incisions are closed with sutures, and a splint may be applied to maintain the new shape during healing.
Why Patients Choose It:
- To correct nasal asymmetry or deformities.
- To improve breathing difficulties caused by structural issues.
- To achieve a nose that is in harmony with the rest of the facial features.
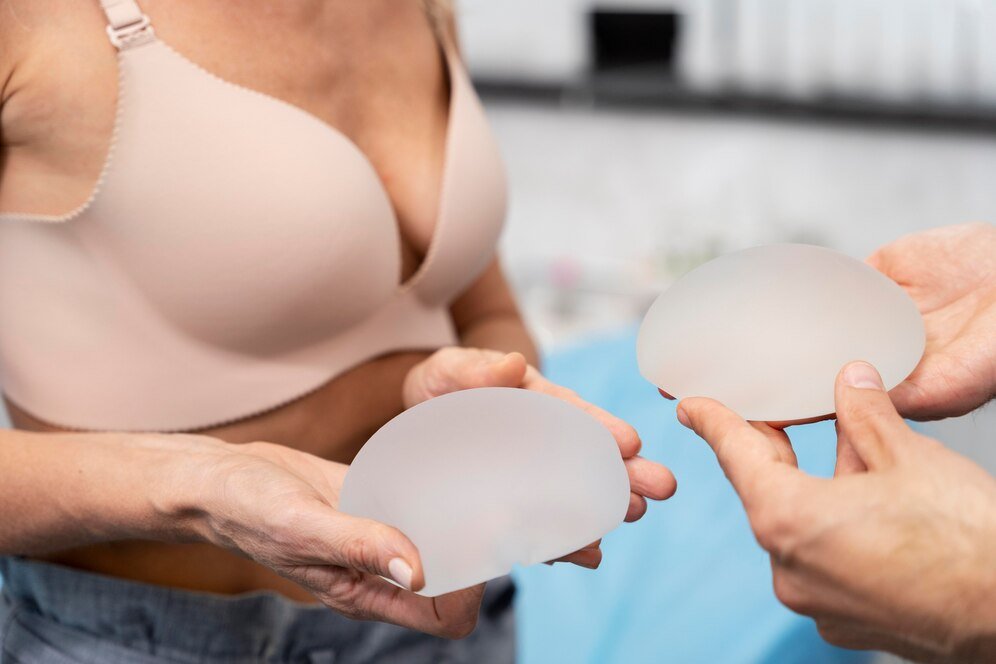
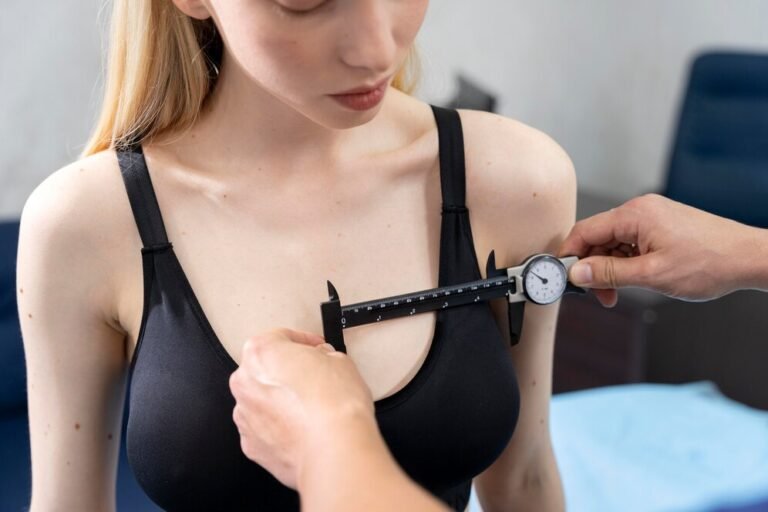
4. Breast Augmentation
Procedure Overview:
Breast augmentation involves using implants or fat transfer to increase the size or improve the shape of the breasts.
Steps:
- Anesthesia: Typically performed under general anesthesia.
- Incisions: Incisions are made in inconspicuous areas (e.g., under the breast fold, around the areola, or in the armpit).
- Implant Insertion: Implants are placed either under the pectoral muscle or directly behind the breast tissue.
- Closure: Incisions are closed with sutures, and dressings are applied.
Why Patients Choose It:
- To enhance breast size for aesthetic reasons.
- To restore breast volume lost after weight reduction or pregnancy.
- To achieve symmetry if breasts are naturally uneven.
5. Breast Lift (Mastopexy)
Procedure Overview:
A breast lift raises and reshapes sagging breasts by removing excess skin and tightening the surrounding tissue.
Steps:
- Anesthesia: Usually performed under general anesthesia.
- Incisions: Patterns vary, but common techniques involve incisions around the areola, vertically down to the breast crease, and horizontally along the breast fold.
- Tissue Repositioning: The underlying breast tissue is lifted and reshaped.
- Skin Removal: Excess skin is removed, and the remaining skin is tightened.
- Closure: Incisions are closed with sutures, often resulting in a more youthful breast contour.
Why Patients Choose It:
- To correct sagging caused by aging, pregnancy, breastfeeding, or weight fluctuations.
- To improve the firmness and shape of the breasts.
- To restore a more youthful breast profile.
6. Liposuction
Procedure Overview:
Liposuction removes excess fat deposits to contour and reshape specific areas of the body, such as the abdomen, hips, thighs, buttocks, arms, or neck.
Steps:
- Anesthesia: Local anesthesia with sedation or general anesthesia.
- Incisions: Small incisions are made in the targeted area.
- Fat Removal: A cannula (a thin tube) is inserted through the incisions to loosen and suction out fat cells.
- Closure: Incisions are closed with sutures or left open to drain, depending on the technique.
Why Patients Choose It:
- To remove stubborn fat that is resistant to diet and exercise.
- To improve body contours and proportions.
- To enhance self-esteem and body confidence.
7. Tummy Tuck (Abdominoplasty)
Procedure Overview:
A tummy tuck removes excess skin and fat from the abdomen and tightens the abdominal muscles, resulting in a flatter and firmer midsection.
Steps:
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia is typically used.
- Incisions: A horizontal incision is made between the pubic hairline and the navel.
- Muscle Tightening: The underlying abdominal muscles are tightened.
- Excess Skin Removal: Excess skin is removed, and the remaining skin is redraped.
- Closure: The incision is closed with sutures, and dressings are applied.
Why Patients Choose It:
- To remove loose, sagging skin after significant weight loss or pregnancy.
- To tighten weakened or separated abdominal muscles.
- To achieve a smoother, more toned abdominal profile.
8. Buttock Augmentation
Procedure Overview:
Buttock augmentation enhances the size and shape of the buttocks using implants or fat transfer (Brazilian Butt Lift).
Steps:
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia or local anesthesia with sedation.
- Incisions: Incisions are made in well-concealed areas, such as the buttock crease.
- Implant Insertion: If implants are used, they are placed either above or within the gluteal muscle.
- Fat Transfer: For a fat transfer, liposuction is first used to harvest fat from another area of the body, which is then purified and injected into the buttocks.
- Closure: Incisions are closed with sutures.
Why Patients Choose It:
- To enhance the size, shape, and firmness of the buttocks.
- To improve body proportions and symmetry.
- To boost confidence and achieve a desired body contour.
9. Arm Lift (Brachioplasty)
Procedure Overview:
An arm lift reduces excess skin and fat between the underarm and the elbow, resulting in a more toned and proportionate appearance.
Steps:
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia or local anesthesia with sedation.
- Incisions: Incisions are typically made on the inside or back of the arm, extending from the underarm to the elbow.
- Fat Removal and Skin Tightening: Liposuction may be used to remove fat, and excess skin is trimmed away.
- Closure: Incisions are closed with sutures, and the arms are bandaged.
Why Patients Choose It:
- To correct sagging underarm skin, often referred to as “bat wings.”
- To improve the contour and appearance of the upper arms.
- To regain confidence in wearing sleeveless clothing.
10. Thigh Lift
Procedure Overview:
A thigh lift reshapes the thighs by reducing excess skin and fat, resulting in smoother skin and better-proportioned contours.
Steps:
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia is commonly used.
- Incisions: Incisions are typically made in the groin area, extending downward around the thigh.
- Skin Removal and Fat Reduction: Excess skin is removed, and liposuction may be used to reduce fat deposits.
- Closure: Incisions are closed with sutures, and the legs are bandaged.
Why Patients Choose It:
- To address sagging skin and fat deposits on the thighs, often after significant weight loss.
- To achieve a more toned and contoured appearance.
- To enhance self-esteem and comfort in clothing.
11. Neck Lift (Platysmaplasty)
Procedure Overview:
A neck lift addresses sagging skin, excess fat, and muscle banding in the neck, providing a more youthful and defined neckline.
Steps:
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia or local anesthesia with sedation.
- Incisions: Incisions are typically made around the ears and sometimes under the chin.
- Muscle Tightening and Fat Removal: The platysma muscle may be tightened, and excess fat is removed.
- Skin Redraping: Excess skin is removed, and the remaining skin is re-draped.
- Closure: Incisions are closed with sutures, and the neck is bandaged.
Why Patients Choose It:
- To correct loose, sagging skin and muscle bands in the neck.
- To achieve a more defined jawline and youthful appearance.
- To complement the results of a facelift.
12. Chin Augmentation
Procedure Overview:
Chin augmentation enhances the size and shape of the chin using implants or injectable fillers to improve facial balance.
Steps:
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia or local anesthesia with sedation.
- Incisions: Incisions are typically made under the chin or inside the mouth.
- Implant Placement: A chin implant is placed over the bone to enhance the chin’s projection and shape.
- Closure: Incisions are closed with sutures.
Why Patients Choose It:
- To improve a weak or recessed chin.
- To enhance facial symmetry and balance.
- To boost confidence and improve overall facial aesthetics.
Cosmetic surgery offers a wide array of options for those seeking to enhance their appearance and self-confidence. Each procedure is tailored to meet the unique needs and goals of the individual, with careful consideration of the desired outcome and the safest, most effective techniques available. Whether motivated by aesthetic desires, functional improvements, or a combination of both, cosmetic surgery can provide transformative results.